CLASSIFICATION OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES
Trials
Created on - 09 May, 2016
1. Van Praagh & Vlad Segmental Approach
• Visceroatrial: S-Solitus, I-Inversus, A-Ambiguus
• Ventricular Topology: D loop & L loop
• Great Vessels: S-Solitus, I-Inversus, D-Dextro, L-Levo
2. Anderson Sequential Segmental Approach
• Atrial
• Atrioventricular
• Ventriculoarterial - Concordant
Discordant
Ambiguus/Mixed
• Cardiac Position - Dextrocardia, Levocardia, Mesocardia
3. Segmental system of Classification of CHD
• Great Veins
• Atria
• Atrioventricular junctions
• Ventricles
• Ventriculoarterial junction
• Great Arteries
Acyanotic: ASD, VSD, PDA, AS, MS, Co-arctation of aorta, AP window
Cyanotic: TOF, TGA, TAPVC, Tricuspid Atresia, HLHS, Ebstein's anomaly, Truncus Arteriosus, PS.
4. AHA Classification
• Septal - ASD, VSD
• Obstructive - PS, AS
• Cyanotic - TOF, TGA
5. Generic Classification
• Hypoplasia: HLHS, HRHS
• Obstructive Defects: PS, AS
• Septal defects
• Cyanotic defects
• Condition of vessel: coarctation of aorta, TAPVC, PAPVC
• Constellation of multiple defects: TOF
6. Other Classification
• L-R shunts
• R-L shunts
• Left Heart Obstructive lesions - MS, AS
• Right Heart Obstructive lesions - PS, TS
• Single Ventricle
• Others - Vascular rings
7. Classification (as in J.Perloff)
• Acyanotic without shunt
• Acyanotic with shunt
• Cyanotics
8. Classification (as in Hurst)
• Intracardiac communication between systemic and pulmonary circulations - ASD, VSD
• Extra cardiac communication - PDA
• Valvular & Vascular malformations of left side - Coarctation of aorta, Valvular AS , Supravalvular AS, Subvalvular AS, Bicuspid AS.
• Valvular & Vascular malformations of right side - TOF, Ebstein's Anomaly.
• Anomalies of pulmonary venous connection - TAPVC
• Malposition of cardiac structures - TGA, cTGA, DORV
• Coronary anomalies - ALCAPA, coronary AVF.
9. Duke Echocardiographic Classification
A) When chambers and valves are in normal sequence and position - When shunting is predominant - ASD, VSD, PDA
When stenosis is predominant - TA, MA, Coarctation of aorta, TAPVC
B) When not in normal position and sequence Below atria & ventricle - Univentricular heart, ccTGA Between ventricles & great vessels - TOF, DORV, TGA
10. Classification
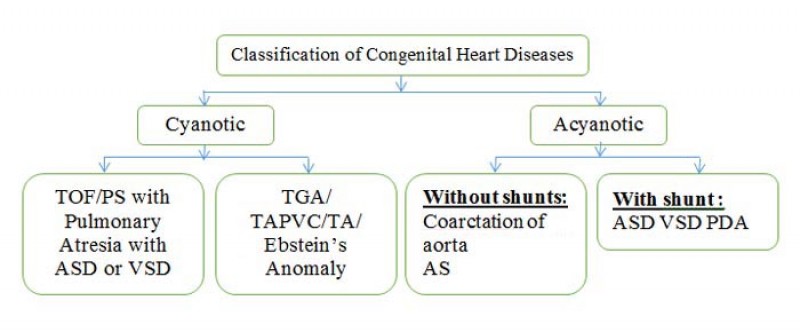
11. Classification of CHD
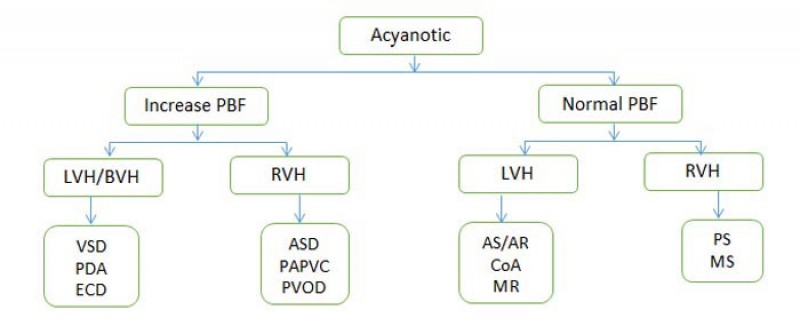
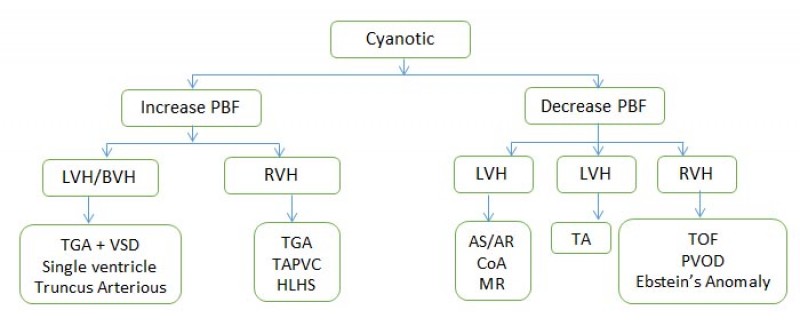
12. Left to Right shunts are sometimes also classified as
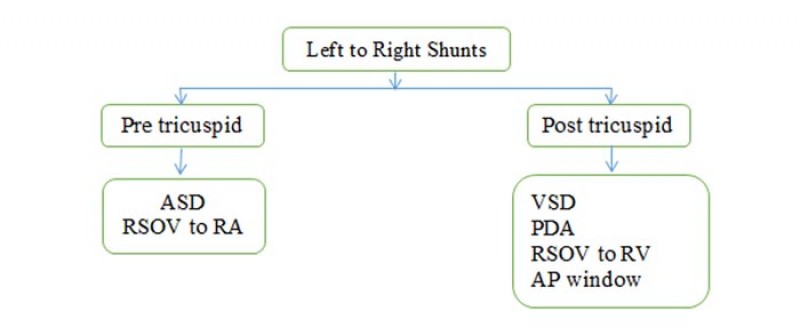
- by Dr Amarja
© Copyright 2025 by Cardiacanaesthesia.in
CONTACT US • ABOUT US • DISCLAIMER • CONFERENCES 2025 •